Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is one of the main evidence based psychological therapies recommended by NICE Guidance (www.nice.org.uk) for treating common mental health problems.
CBT aims to help someone to better understand and develop insights into their thoughts, behaviours and feelings, to see patterns and links that contribute to maintaining difficulties such as depression/anxiety etc. Then the focus is on how to develop and practice a variety of techniques that are put into place in between sessions, helping to break out of any unhelpful cycles and patterns. Over time and with practice, this leads to a reduction in symptoms and improved wellbeing.
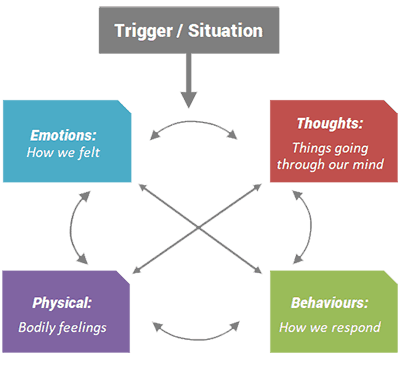
A combination of techniques are used that help to identify and alter: – Unhelpful behaviours – our responses/what we do, or don’t do – Unhelpful thought processes, beliefs and assumptions, referred to as cognitions. Our behaviours and cognitions are known to be closely linked and strongly influence our emotional and physiological state – how we feel. The below diagram demonstrates the basic ‘five areas’ model.
CBT aims to help someone to better understand and develop insights into their thoughts, behaviours and feelings, to see patterns and links that contribute to maintaining difficulties such as depression/anxiety etc. Then the focus is on how to develop and practice a variety of techniques that are put into place in between sessions, helping to break out of any unhelpful cycles and patterns. Over time and with practice, this leads to a reduction in symptoms and improved wellbeing.
A combination of techniques are used that help to identify and alter: – Unhelpful behaviours – our responses/what we do, or don’t do – Unhelpful thought processes, beliefs and assumptions, referred to as cognitions. Our behaviours and cognitions are known to be closely linked and strongly influence our emotional and physiological state – how we feel. The below diagram demonstrates the basic ‘five areas’ model.
Research also shows that practicing CBT is likely to have a longer term benefit than the use of antidepressant medication and can help to prevent similar difficulties in the future.
Although CBT is classed as a type of ‘talking therapy’, it is in fact very different to what is commonly known as ‘counselling’. There are many types of counselling, but CBT in particular is a structured therapy in comparison, encompassing set goals for each session and agreed homework tasks. The in between session tasks are an essential part of gaining benefit and change from CBT. CBT helps to equip someone with resources to manage their wellbeing more independently and empower them to implement effective strategies that can lead to longer term improvements. Like becoming their own therapist!
Although CBT is classed as a type of ‘talking therapy’, it is in fact very different to what is commonly known as ‘counselling’. There are many types of counselling, but CBT in particular is a structured therapy in comparison, encompassing set goals for each session and agreed homework tasks. The in between session tasks are an essential part of gaining benefit and change from CBT. CBT helps to equip someone with resources to manage their wellbeing more independently and empower them to implement effective strategies that can lead to longer term improvements. Like becoming their own therapist!